 |  |  |
|---|
Hepatitis B is a viral infection of the liver and approximately 1/3 of a billion people world wide have a chronic infection.
Chronic Hepatitis B infections can lead to liver cirrhosis, cancer and death.
Hepatitis B infection is spread to humans by mixing bodily fluids or blood by accidents, blood transfusions, sexual intercourse, tattooing, acupuncture and reusing needles or medical equipment.
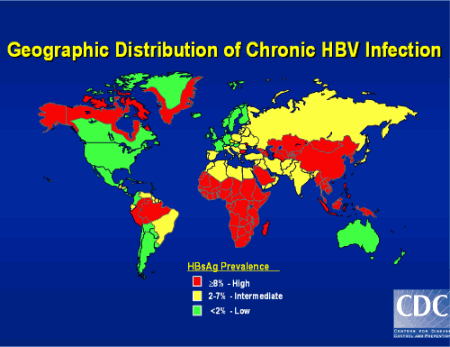
Hepatitis B infections are more common in certain parts of the world with up to 10% of people in SE Asia being affected.
Hepatitis B viral disease is incurable and can lead to acute infection, liver cirrhosis, liver cancer and death over time.
Other symptoms include jaundice ( yellow eyes), weight loss, loss of appetite, tiredness, fever, dark urine and light coloured stools.
The best way to reduce the risk of infection is by being vaccinated as it is not always possible to prevent accidents
The Health and Safety Executive lists the following types of work at risk of blood/ bodily fluid contact:
-
health care (hospitals, clinics, dental surgeries, pathology departments,)
-
emergency services (ambulance/fire/police/rescue)
-
community nursing, acupuncture, chiropody, associated cleaning services)
-
hairdressing and beauticians’ work
-
custodial services (prisons/detention centres/homes)
-
education
-
laboratory work (forensic, research etc)
-
local authority services (street cleaning/park maintenance/refuse disposal/public
-
lavatory maintenance)
-
medical/dental equipment repair
-
military
-
mortuary work
-
embalming and crematorium work
-
first aid
-
needle exchange services
-
plumbing
-
sewage processing
-
social services
-
tattooing, ear and body piercing
-
vehicle recovery and repair
Hepatitis B Vaccination (Non-live)
Primary Hepatitis B vaccination is a course of three vaccinations given over a few weeks to a few months depending on age.
It is a very safe vaccination and can be given from birth.
For those who require vaccination for occupational purposes a blood immunity check is strongly recommended as vaccination is 90% effective but not always 100% effective.
Some people do NOT respond to the vaccination.
The chances of not responding to the vaccine is associated with being over the age of 40, male gender, obesity, smoking, chronic illness and a chronic Hepatitis B infection.
Therefore a blood test undertaken 4-8 weeks after the third dose is recommended to check for a sufficient immune response.
Without this check, it is impossible to know if workers have enough immunity to work safely.
We offer a discounted rate for Occupational Health works taking up the vaccination and immunity check together
